In the ever-evolving landscape of global commerce, basic industries stand as the foundational pillars that support economies worldwide. These industries are integral to the production of essential goods and raw materials, serving as the bedrock upon which other sectors build and thrive. As we navigate through 2024, understanding the role and impact of basic industries becomes increasingly crucial for businesses, policymakers, and academics alike.
Definition of Basic Industries

Basic industries refer to sectors involved in the extraction and production of raw materials that are fundamental to other industries’ manufacturing processes. These include areas such as agriculture, mining, oil and gas, forestry, and chemical production. The primary focus of basic industries is to supply the essential inputs required for the production of goods and services in the broader economy.
To elaborate, basic industries are characterized by their role in providing foundational materials without significant alteration or processing. They differ from non-basic industries, which typically produce goods and services for immediate consumption or further processing within the local economy.
Understanding Basic Industries
The concept of basic industries dates back to the dawn of industrialization, where they played a pivotal role in shaping modern economies. During the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries, societies transitioned from agrarian economies to industrial powerhouses. Basic industries such as mining, agriculture, and forestry were at the forefront of this transformation, supplying essential raw materials like coal, iron, and timber.
These industries laid the groundwork for the development of infrastructure, transportation, and manufacturing sectors. For instance, the abundance of coal and iron ore fueled the growth of the steel industry, which in turn facilitated the construction of railways and buildings. The historical significance of basic industries is evident in their contribution to economic expansion, technological advancements, and the enhancement of living standards during that era.
For more detailed examples of basic industries, you can read our post: Basic Industries Examples: 4 Pillars of Global Prosperity.
Key Characteristics
Basic industries are distinguished by several key characteristics that set them apart from other sectors:
- Resource Extraction and Production: They focus on extracting and producing raw materials from natural resources. This includes activities like mining minerals, harvesting timber, and drilling for oil and gas.
- Foundation of the Supply Chain: Serving as the initial link in the production chain, they provide essential inputs for secondary industries that manufacture finished goods.
- Capital Intensive: Operations often require substantial investment in machinery, technology, and infrastructure to efficiently extract and process raw materials.
- Global Economic Impact: Products from basic industries are frequently traded on international markets, influencing global commodity prices and trade dynamics.
- Employment Generation: They offer numerous job opportunities, often in regions where alternative employment may be scarce, contributing to regional economic development.
- Regulatory and Environmental Considerations: Due to their interaction with natural resources, these industries are subject to environmental regulations and sustainability practices.
Understanding these characteristics is crucial for comprehending how basic industries operate and their role in the broader economic context.
Importance in the Global Economy
The significance of basic industries in the global economy cannot be overstated. They serve as the starting point of the supply chain, enabling the production of a wide array of products that drive economic growth. By supplying raw materials, basic industries facilitate the functioning of manufacturing sectors, support infrastructure development, and contribute to technological advancements.
Basic industries contribute significantly to a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). For instance, in many developing nations, agriculture is a primary source of income and plays a crucial role in boosting the GDP. A detailed breakdown of the GDP share by industry in the U.S. in 2023 highlights the significance of various sectors.
Moreover, basic industries are often significant employers, providing numerous job opportunities across various skill levels. They play a vital role in trade, with many countries relying on exports from these sectors to bolster their economies. For instance, the mining industry in Australia and the oil industry in the Middle East are prime examples of how basic industries can shape national economic landscapes.
If you’re interested in exploring the job market within these sectors, including the number of available positions and career prospects, visit our article on How Many Jobs Are Available in Basic Industries.
Environmental sustainability is another critical aspect. As the world shifts towards greener economies, basic industries are at the forefront of adopting sustainable practices. Innovations in renewable energy and eco-friendly extraction methods are transforming how these industries operate, ensuring they continue to meet global demands responsibly.
Basic Industries vs. Non-Basic Industries
Differentiating between basic and non-basic industries is essential to grasp their unique contributions to the economy.
The main distinction lies in their economic impact:
- Revenue Generation: Basic industries generate revenue from outside the local economy, which can lead to economic expansion. Non-basic industries rely on the spending power within the local community.
- Employment Patterns: Jobs in basic industries are often specialized and may offer higher wages due to the technical skills required. Non-basic industries provide a broader range of employment opportunities, often with more entry-level positions.
Understanding this difference is vital for policymakers and business leaders when planning economic development strategies. It highlights the importance of nurturing both sectors to ensure a balanced and resilient economy. If you’re interested in learning about specific companies within the basic industries field, feel free to visit our post on What Companies Are in the Basic Industries Field.
Sectors Within Basic Industries

Agriculture
Agriculture is one of the most fundamental sectors within basic industries. It involves the cultivation of crops and the rearing of livestock to produce food, fiber, and other essential products. This sector supplies raw materials like grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy, which are crucial for the food processing industry and other manufacturing sectors.
Key aspects of the agriculture sector include:
- Crop Production: Growing plants for food, fuel, and industrial materials.
- Livestock Farming: Raising animals for meat, dairy, and other animal products.
- Agrotechnology: Implementing advanced technology to improve yield and efficiency.
- Sustainable Farming: Adopting eco-friendly practices to preserve soil health and biodiversity.
Agriculture not only feeds the global population but also provides employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas. It plays a significant role in the economies of many countries by contributing to GDP and trade balances.
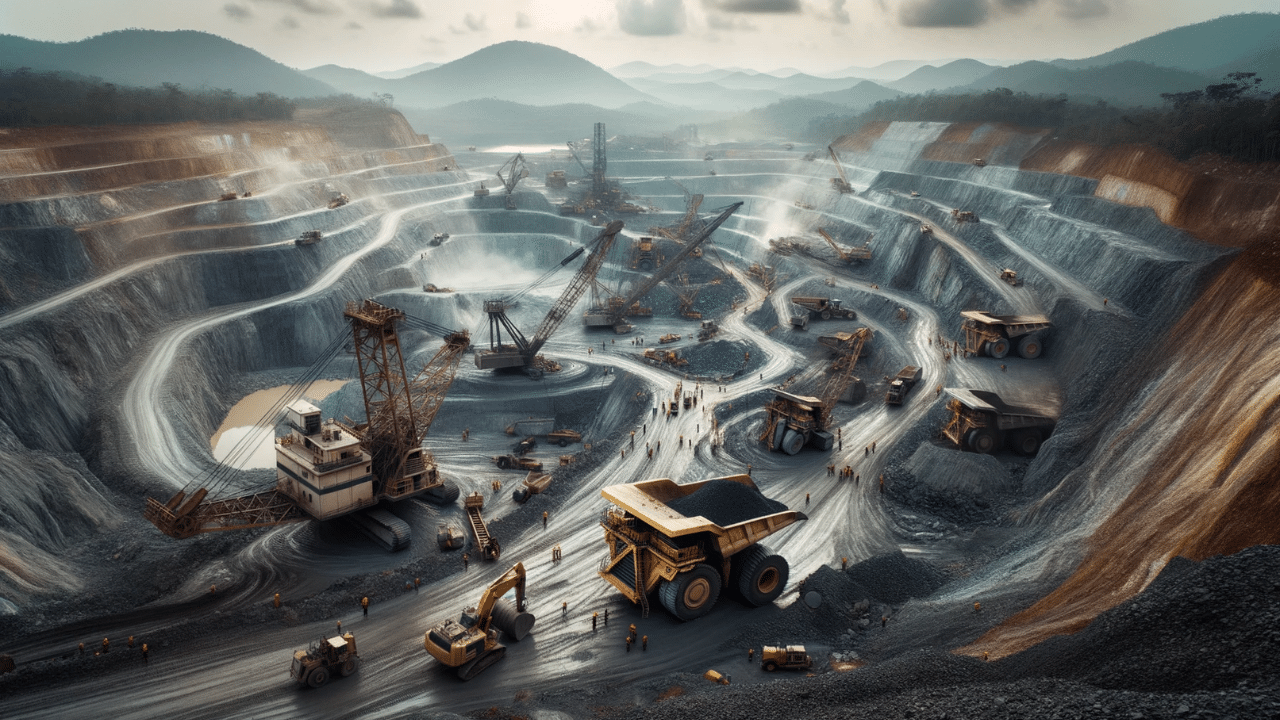
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals and other geological materials from the earth. This sector supplies essential raw materials like metals, coal, and gemstones, which are foundational to construction, manufacturing, and energy production.
Key aspects of the mining sector include:
- Mineral Exploration: Identifying and assessing mineral deposits.
- Extraction Techniques: Methods such as surface mining and underground mining.
- Processing and Refining: Converting raw minerals into usable forms.
- Environmental Management: Implementing practices to reduce ecological impact.
The mining industry is capital-intensive and often involves complex operations requiring advanced technology and specialized labor. It significantly impacts local and global economies by providing raw materials essential for various industries.
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas sector focuses on the exploration, extraction, refining, and marketing of petroleum products and natural gas. These resources are vital for energy production, transportation, heating, and as raw materials for the petrochemical industry.
Key aspects of the oil and gas sector include:
- Exploration and Drilling: Locating and extracting oil and natural gas reserves.
- Refining Processes: Converting crude oil into usable fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
- Distribution Networks: Transporting products via pipelines, ships, and trucks.
- Energy Transition: Shifting towards sustainable energy sources to reduce carbon emissions.
The oil and gas industry plays a pivotal role in global economics and geopolitics. It offers lucrative career opportunities due to its scale and complexity. For insights into the highest-paying jobs within this sector, check out our post on Best Paying Jobs in Basic Industries.
Forestry
Forestry involves the management, conservation, and sustainable harvesting of forests to produce timber and other forest products. This sector supplies raw materials for construction, paper production, and various other industries.
Key aspects of the forestry sector include:
- Timber Production: Harvesting trees for lumber and wood products.
- Reforestation: Planting trees to replenish harvested areas.
- Wildlife Conservation: Protecting habitats and biodiversity.
- Non-Timber Products: Collecting resources like resins, fruits, and medicinal plants.
Forestry is crucial for environmental sustainability, as forests act as carbon sinks and help regulate the global climate. The sector also supports the livelihoods of communities in forested areas.
Chemical Production
Chemical production involves transforming raw materials like oil, natural gas, minerals, and water into chemicals used in a multitude of products and industries. This sector is essential for manufacturing goods ranging from plastics and pharmaceuticals to agricultural chemicals.
Key aspects of the chemical production sector include:
- Basic Chemicals: Producing acids, alkalis, and other substances used as industrial inputs.
- Specialty Chemicals: Creating chemicals for specific applications like adhesives and coatings.
- Pharmaceuticals: Manufacturing medicinal drugs and health-related products.
- Research and Development: Innovating new chemical processes and products.
The chemical industry is integral to modern life and technological advancement. It also provides numerous employment opportunities across various skill levels.
Challenges Facing Basic Industries
Environmental Concerns
One of the most pressing challenges facing basic industries today is the growing concern over environmental sustainability. Industries such as mining, oil and gas, and chemical production significantly impact the environment through resource depletion, habitat destruction, and pollution.
Key environmental concerns include:
- Climate Change: Emissions of greenhouse gases from industrial activities contribute to global warming, leading to extreme weather events and ecological imbalances.
- Pollution: Release of pollutants into air, water, and soil affects biodiversity and human health.
- Resource Depletion: Over-extraction of natural resources leads to scarcity and threatens the long-term viability of industries.
To address these issues, companies are adopting sustainable practices such as:
- Implementing Renewable Energy Sources: Transitioning to solar, wind, or hydro power to reduce carbon footprints.
- Eco-friendly Technologies: Investing in cleaner production methods and waste management systems.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Emphasizing recycling and responsible sourcing of materials.
Understanding these environmental challenges is crucial for the future of basic industries. Stakeholders are increasingly demanding transparency and responsibility, pushing companies to innovate and adapt.
Technological Disruption
Technological advancements are both a boon and a challenge for basic industries. While they offer opportunities for increased efficiency and new business models, they also pose threats to traditional operations.
Key aspects of technological disruption include:
- Automation and AI: Machines and artificial intelligence are replacing manual labor, leading to job displacement but increasing productivity.
- Digitalization: Adoption of digital technologies improves supply chain management but requires significant investment and training.
- Innovation in Materials: Development of alternative materials (e.g., biodegradable plastics) can disrupt traditional markets.
These changes necessitate a shift in workforce skills and can create a gap between current employee capabilities and new job requirements. Companies must invest in retraining programs to help employees adapt to new technologies.
Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory challenges are a significant concern for basic industries, often affecting operational efficiency and profitability.
Key regulatory hurdles include:
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter laws on emissions and waste disposal require companies to invest in cleaner technologies, increasing operational costs.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs and trade agreements can impact the import and export of raw materials, affecting supply chains.
- Labor Laws: Regulations concerning worker safety, wages, and working conditions require compliance that can increase administrative burdens.
Navigating these regulations requires strategic planning and often collaboration with government bodies. Companies that proactively engage with policymakers can sometimes influence regulations in a way that balances economic and environmental interests.
For an in-depth look at whether basic industries offer a promising career path, read our post Is Basic Industries a Good Career Path?
Frequently Asked Questions
With the growing significance of basic industries in the global landscape, many individuals have queries about the sector, its prospects, and its challenges. Here, we address some of the most commonly asked questions to provide clarity and insights.
u003cstrongu003eWhat is the definition of Basic industries ?u003c/strongu003e
Basic industries are those that produce raw materials or essential products that are used by other industries for manufacturing and production. These industries form the backbone of the economy, supplying foundational resources like metals, chemicals, and agricultural products.
What is an example of a basic sector ?
An example of a basic sector is u003cstrongu003eminingu003c/strongu003e, where raw materials like coal, iron ore, or copper are extracted and then used by other industries for further processing into finished products.
A quick overview of the topics covered in this article.
Latest Posts
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get valuable insights and business guidance sent to your email.